Low-frequency noise immissions
The characteristic of low-frequency noise immissions inside of rooms is influenced on the one hand by the properties of the separating constructional elements, such as frequencies of coincidence and natural frequencies. These frequencies mainly depend on the geometrical dimensions of the constructional element and on the material. In many cases, at low frequencies windows dominate the sound insulation. Windows operate as low-pass filters. On the other hand, besides the sound absorbing properties of the room setup, the natural frequencies (modes) of the receiving room have a strong influence on the amplitude and the distribution of the sound pressure inside the room.
Therefore, the relevant parts of a reliable prognosis are:
- the knowledge of the spectral noise emission values (sound power),
- the calculation of the sound propagation (energetic according to DIN ISO 9613-2 or coherent, e. g. according to Nord 2000,
- the calculation of the sound insulation of the separating outer and inner constructional elements (under consideration of natural frequencies and frequencies of coincidence), also depending on the angle of sound incidence as well as
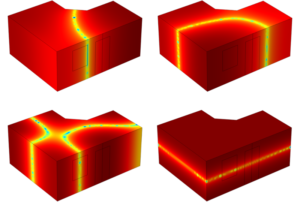
- the calculation of the eigenmodes of a room in need of protection, also for complex geometries.
Measurements
The listed calculations are partially connected with a considerable effort as well as specific uncertainties, especially the two latter ones. Therefore, within a research project on behalf of the state office for the environment, agriculture and geology (LfULG), statistical results were gained. Based on measurements at 35 rooms representative for Saxony, sound pressure level differences between outside and inside were determined. These results allow to define a maximum sound pressure level outside which complies with the indicative values inside with adequate certainty.
You can find the detailed investigation report here:
To publication of results of investigations